Resonant access to a solid-state quantum system with no need for laser background rejection
2023/08/15
Quantum Photonics Group of BAQIS, led by Chief Scientist Dr Zhiliang Yuan and in collaboration with the Institute of Semiconductors CAS, has recently published a research article entitled "Mollow triplets under few-photon excitation" in the prestigious journal of Optica, reporting the first observation of Mollow triplets in resonant fluorescence of a solid-state quantum system without a need for laser background rejection.
Resonant excitation is an essential tool in the development of semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) for quantum information processing. However, the resonance excitation technique typically requires cross-polarization filtering, which not only halves the collection of the resonantly scattered signal but also, more importantly, precludes QD's applications for polarization-based protocols such as generation of photonic cluster states using charged excitons.
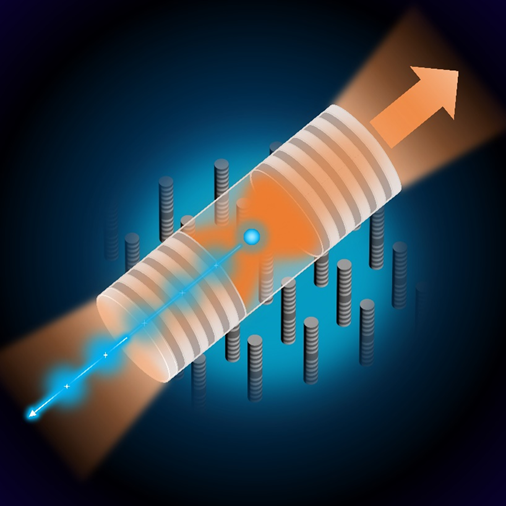
Fig. 1 Resonant excitation of semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) with an ultra-low cavity reflectivity micropillar.
Exploiting an ultra-low cavity reflectivity micropillar (0.89%), the authors demonstrate the first observation of Mollow triplets for QDs without resort to any laser background rejection technique. In weak excitation, we achieve a signal to background ratio up to 55 and device responsivity of 14.4 %, i.e., the device resonantly scattered 0.14 photons for every incident laser photon. Raising the excitation to the few-photon level, the QD response is brought into saturation where the authors observe the Mollow triplets as well as the associated cascade single photon emissions. Observation of the Mollow triplets implies the feasibility of using deterministic pulsed excitation for efficient generation of single photons, with lossless encoding via modulating the polarization of the excitation beam. A complete access to the QD signal could allow excitation and collection of photons in arbitrary polarizations, which is crucial step towards generation of photonic cluster states.
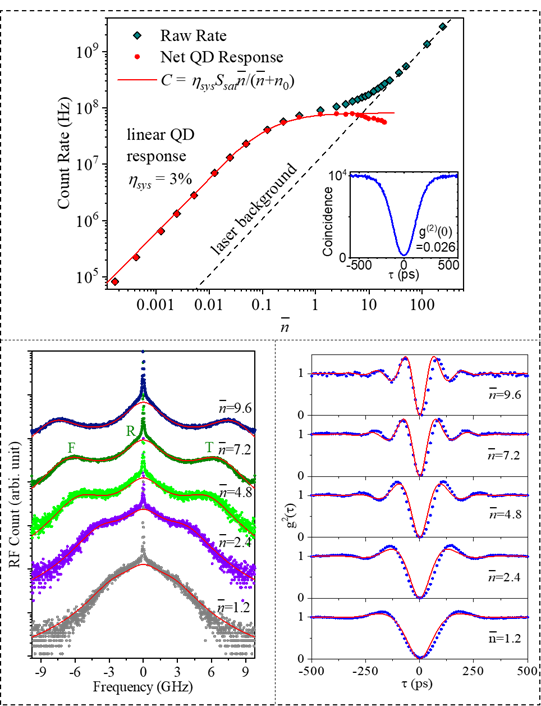
Fig. 2 The Mollow triplets under few-photon excitation
Dr. Bang Wu and Dr. Xu-jie Wang, associate researchers at BAQIS (Beijing Quantum Information Science Research Institute), contributed equally to this project. Dr. Zhiliang Yuan, chief scientist at BAQIS, supervised the project. Other co-authors include Liu Li and Wang Wenyi, engineers at BAQIS, Huang Guoqi, an intern PhD student from Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Hanqing Liu, a doctoral student, as well as Haiqiao Ni and Zhichuan Niu, researchers from the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences. This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Link to the article: https://opg.optica.org/optica/fulltext.cfm?uri=optica-10-8-1118&id=536522
 中文
中文 Email
Email QCloud
QCloud Log in
Log in
