QSDC research group make progress in the field of access authentication for quantum communication networks
2024/11/19
Recently, Professor Gui-Lu Long and Associate Researcher Min Wang from the Quantum Secure Direct Communication (QSDC) group at the Beijing Academy of Quantum Information Sciences (BAQIS) made progress in access authentication for quantum communication networks. They developed a quantum-channel access authentication scheme with comprehensive security features by integrating quantum communication with post-quantum cryptography and encoding digital signatures into quantum states for transmission and verification. The findings were published online On November 7, 2024, in Science China Information Sciences under the title "Lattice-based access authentication scheme for quantum communication networks."
Secure and efficient access authentication is fundamental to ensuring the safety and functionality of communication networks. Such schemes require robust public-key cryptographic algorithms, including key establishment and digital signature mechanisms. However, traditional public-key cryptography is vulnerable to quantum computing threats, rendering it unsuitable for quantum-safe access authentication in quantum communication networks.
On the other hand, after years of development, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has released its first set of post-quantum encryption and digital signature standards. These include lattice-based public-key encryption and key encapsulation algorithms, such as CRYSTALS-KYBER, and digital signature algorithms, such as CRYSTALS-Dilithium. The migration from traditional public-key cryptography to post-quantum cryptography is already underway.
This has made it essential to explore the effective integration of quantum communication with post-quantum cryptography, advance research into post-quantum cryptographic migration, and design quantum-safe access authentication schemes with comprehensive security features for quantum networks.
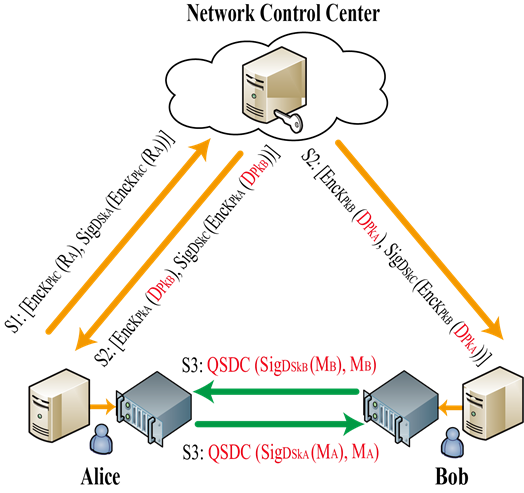
Figure1 Access authentication scheme for the QSDC network
The proposed access authentication scheme uses lattice-based cryptographic algorithms, namely CRYSTALS-Dilithium and CRYSTALS-KYBER, as its core algorithms, involving real-time interaction with the network control center (NCC) during authentication. First, the NCC’s public keys are preconfigured in the communication devices that intend to join into the network. Users then register by sending their public keys to the NCC. During authentication, the communication initiator encrypts and sends a communication request to the NCC, which subsequently encrypts and distributes the recipient's public keys based on the request. After receiving each other's public keys, both parties encode signature information into quantum states and transmit them through the quantum channel. If verification succeeds, mutual authentication of the quantum channel is established.
This scheme successfully combines quantum communication with post-quantum cryptography and offers security properties such as mutual authentication, conditional anonymity, data confidentiality, data integrity, unforgeability, and undeniability. The seamless integration of these two quantum security technologies offers a novel approach to constructing quantum-safe communication networks using present-day technologies.
The first author of this paper is Associate Researcher Min Wang from BAQIS, and the corresponding authors are Associate Researcher Min Wang from BAQIS and Professor Gui-Lu Long from BAQIS and Tsinghua University. This work was supported by the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by China Association for Science and Technology.
Paper link:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-024-4177-5
 中文
中文 Email
Email QCloud
QCloud Log in
Log in
